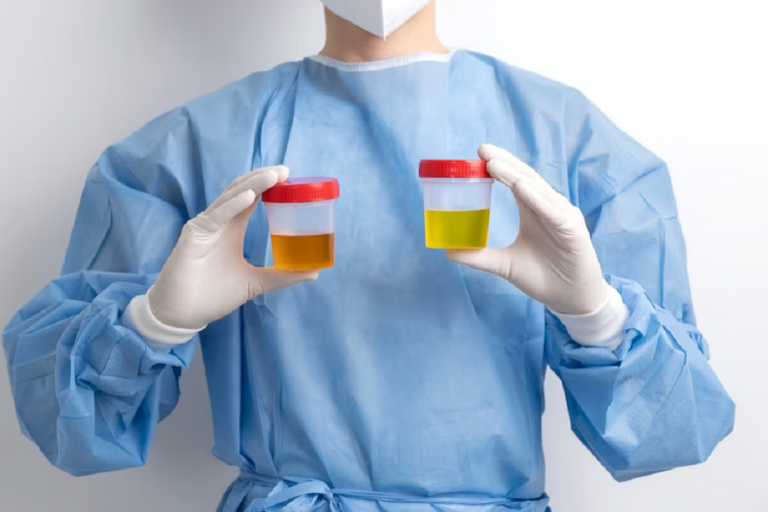

It can be frightening to see blood in your urine, which is usually caused due to hematuria. Blood in the urine is also called Hematuria. In many cases, it is curable and not life-threatening, but sometimes it can be a sign of a serious illness.
A clear understanding of blood in the urine causes and symptoms will allow you to know when to acquire medical help.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are quite prevalent and happen when bacteria enter the urethra and infect the urinary tract, most commonly the bladder.
The infections can impact different parts of the urinary tract; sometimes, they can even spread to your kidneys and make you really sick.
Only a small amount of blood can change the color of urine and make it pink, red, or cola-colored. The bleeding is not quite painful, but if blood clots travel through the urethra and get passed in the urine, that can really hurt.
What Is Blood in the Urine?
If you find blood in the urine, it may occur due to a kidney infection or because of problems in other parts of the urinary tract, such as bladder cancer.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are the most prevalent cause of hematuria. Since the urinary tract comprises the ureters, kidneys, and bladder, infection occurring anywhere in that system can result in blood in the urine.
What Is Haematuria?
Peeing Blood UTI (Urinary Tract Infection) is a medical condition that occurs due to the presence of cells of blood in the urine. This issue usually takes place when kidneys or other parts of the urinary tract leak blood cells into the urine.
Symptoms of a UTI
Common symptoms of UTI include:
- Pain or burning sensation while peeing.
- Bad-smelling or cloudy urine.
- Presence of pus or blood in the urine.
- Soreness, pain, or cramps in the lower belly when a person pees.
Fortunately, UTI is a curable medical problem and is generally treated with medicines (antibiotics). However, it is necessary to seek medical help at the right time. Therefore, if you experience any of the above-mentioned symptoms while peeing, consult your healthcare professional as soon as possible.
What Causes Bleeding During a UTI?
When a person suffers from UTI, the bacteria infect his urinary tract, causing inflammation, by leaking red cells of blood in the urine. If there’s a small amount of blood in the urine, it is usually not visible to the naked eye. But patients can still experience symptoms of UTI.
Though bacteria are the most common cause of UTIs, in some cases, fungi can also infect the urinary tract.
Treating UTI Bleeding
The only way to eliminate a UTI is to properly treat it. Antibiotics are considered the best treatment option for urinary tract infections. However, when antibiotics no longer work to treat UTIs, then other complicated treatments are acquired.
1. Antibiotics
The type of antibiotics healthcare providers prescribe for their patients is usually contingent on their current health status, the kind of bacteria found in their urine, and whether their UTI is complicated or uncomplicated.
Depending on which antibiotic the doctor prescribes, the doses also differ in men and women. Females usually need a single dose that is given as a five-day course. However, in the case of men, antibiotics are usually given for a relatively long time.
Common antibiotics typically used in the treatment of UTIs are classified as Carbapenems (Doripenem, Meropenem, Imipenem, and Ertapenem). Antimicrobials such as Nitrofurantoin, Amikacin, Fosfomycin, and Cefepime may also prove to be a good option.
2. Other Treatments
- Repeat Testing: Doctors typically repeat the urinalysis and antibiotic susceptibility testing if UTI symptoms don’t go away even after antimicrobial therapy.
- Vaginal Estrogen: For women with recurrent UTIs, vaginal estrogen therapy is provided in order to reduce the frequency of UTIs.
How Do Health Care Professionals Diagnose Hematuria?
Healthcare providers begin the diagnosis of hematuria through urinalysis or a urine test in order to detect the presence of blood cells in the patient’s urine.
In some cases, healthcare professionals test the urine sample multiple times to rule out other possibilities and confirm the diagnosis of Hematuria.
Other diagnostic procedures include:
- Physical Exam: This includes a detailed discussion of patients’ health history with their doctor.
- Imaging Tests: An imaging test is often required to detect the reason for the presence of blood in the urine. In such cases, doctors might do an MRI, CT scan, or ultrasound exam.
Home Remedies for Peeing Blood UTI
Apart from medical treatments, there are various home remedies that can ease up your peeing blood UTI symptoms and help alleviate the pain:
- Drink plenty of water.
- Don’t hold your urine.
- Eat garlic.
- Add vitamin C to your diet.
- Avoid foods that can irritate your bladder.
What Actually Reasons Blood in Urine?
Conclusion
Peeing Blood UTI (Urinary Tract Infection) is a common urinary bladder infection that occurs due to the presence of infection-causing bacteria in your urinary tract, which, as a result, causes irritation. It makes the color of your urine look either red, pink, or cola-colored.
However, it is a curable condition that can be reversed with the right medical approach. But untreated hematuria can result in complicated problems, especially if the underlying cause is more severe.
Therefore, doctors should do a proper diagnosis before giving any kind of treatment. If the cause is something like kidney infection or cancer, early detection can minimize the chances of severe complications by leading to the right treatment.
FAQs
Is Blood in Pee Serious?
Most cases of blood in the urine are not serious and don’t require emergency treatments. However, if someone is experiencing symptoms such as extreme pain while urinating, lightheadedness, or soreness, he should see a doctor instantly.
What Does UTI Bleeding Look Like?
UTIs can cause bleeding in the urine, making it look either brown, red or pink. With a UTI, patients may also feel pain and a burning sensation while urinating.
Can Drinking Water Stop Blood in Urine?
Doctors usually advise patients to drink lots of water for urine problems or blood in the urine, but it doesn’t always prove to be helpful.
If you notice blood, you should first see your healthcare provider in order to detect the actual cause and rule out any underlying problems.