
Sleep and Aging for older persons, variations in the quantity and quality of their sleep are typical as they age.
As we age, it is common for our sleep patterns to change, and many people find that they have difficulty staying asleep. This can be frustrating and lead to daytime fatigue and other health issues.
There are several reasons why older adults may have trouble staying asleep. One common reason is changes in the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, which can make it more difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep.
Other factors contributing to sleep disturbances in older adults include medical conditions such as sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, chronic pain, and medications that can interfere with sleep.
Additionally, changes in lifestyle, such as retirement and reduced physical activity, can also impact sleep patterns. Environmental factors, such as noise and light pollution, can also make it more difficult to stay asleep.
While sleep disturbances are common in older adults, there are steps that can be taken to improve sleep quality, such as establishing a regular sleep routine, avoiding stimulating activities before bedtime, and creating a comfortable sleep environment.
It is important for older adults to discuss any sleep issues with their healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and identify appropriate treatment options.
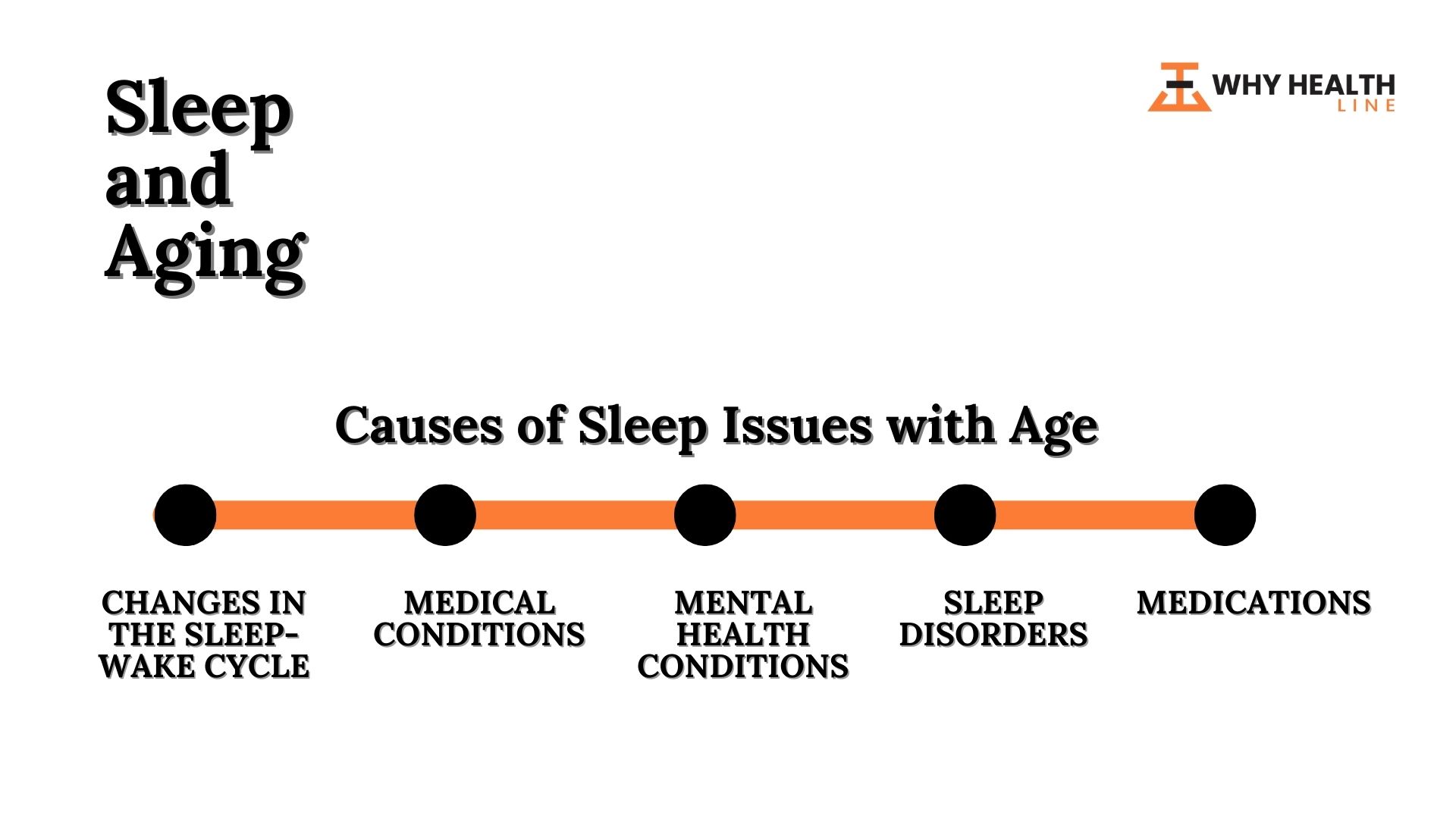
Causes of Sleep Issues by Age
There are several common causes of sleep problems in older adults.
These include:
Changes in the Sleep-Wake Cycle:
As we age, our internal clock shifts, and our sleep-wake cycle changes. This can lead to difficulties falling asleep at night and staying awake during the day.
Medical Conditions:
Many medical conditions that are more common in older adults, such as arthritis, chronic pain, and heart disease, can cause sleep disturbances.
Medications:
Some medications used to treat medical conditions can cause sleep disturbances as a side effect.
Mental Health Conditions:
Anxiety, depression, and other conditions can interfere with sleep.
Sleep Disorders:
Older adults are more likely to develop sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea, restless legs syndrome, and periodic limb movement disorder.
Lifestyle Factors:
Poor sleep hygiene, such as an irregular sleep schedule, lack of physical activity, and excessive caffeine or alcohol intake, can also contribute to sleep problems in older adults.
Speaking with a healthcare provider if you are experiencing sleep problems is important, as they can help identify the underlying cause and provide appropriate treatment.
How to Prevent Insomnia in Aging?
Insomnia is a common problem among seniors, but there are several things they can do to prevent it.
Here are some tips:
Maintain a Regular Sleep Schedule: Seniors should try to go to bed and wake up simultaneously every day. This will help regulate their body clock and make it easier to fall asleep at night.
Create a Comfortable Sleep Environment: Seniors should ensure their bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet. They should also invest in comfortable mattresses and pillows.
Avoid Caffeine and Alcohol: Seniors should limit their intake of caffeine and alcohol, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime. Both substances can interfere with sleep quality and make it harder to fall asleep.
Stay Active During the Day: Regular exercise can help seniors fall asleep faster and stay asleep longer. They should get at least 30 minutes of physical activity every day.
Limit Naps: Seniors should avoid taking long naps during the day, which can disrupt their sleep at night. However, short power naps of no more than 20-30 minutes can be helpful for some people.
Manage Stress: Stress and anxiety can make it hard to fall asleep at night. Seniors should try relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga to manage stress.
Talk to a Doctor: If seniors still have trouble sleeping, they should talk to their doctor. They may recommend a sleep study or prescribe medication to help them sleep.
By following these tips, seniors can improve the quality of their sleep and reduce the risk of insomnia.
FAQs
How Does Sleep Affect Aging?
Sleep plays a crucial role in the aging process, affecting both physical and cognitive aspects. Adequate sleep helps to repair and rejuvenate the body’s cells and tissues, promoting overall health and longevity.
Sleep deprivation, on the other hand, can accelerate the aging process, leading to decreased cognitive function, a weakened immune system, and an increased risk of chronic illnesses such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Sleep also helps to regulate hormone levels, such as growth hormone and cortisol, which are essential for maintaining a healthy metabolism and regulating stress. Thus, ensuring adequate and quality sleep is crucial for healthy aging.
Can Sleep Reduce Aging?
Yes, sleep can reduce aging. During sleep, the body undergoes various restorative processes such as cell repair and the removal of toxins, which can slow down the aging process.
Lack of sleep, on the other hand, can lead to the accumulation of harmful substances and oxidative stress, which can accelerate aging. Moreover, sleep deprivation can lead to the release of stress hormones, which can damage the skin and cause wrinkles.
Therefore, getting sufficient sleep on a regular basis can be an effective way to reduce the effects of aging and maintain a youthful appearance.