Epilepsy is a neurological disorder that is characterized by unprovoking and recurring seizures. Seizures are uncontrolled, short-term, and electrical bursts in the brain’s activity.
Epilepsy is a condition with no specific cure; however, many treatment options are available. Most of the patients suffering from this disease can manage it with the help of medications.
Keep reading to learn everything related to this disorder. The more you understand this condition, the more you can identify seizures and help save lives.
What Is Epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a mental illness in which the brain’s electrical rhythms become disrupted, resulting in unprovoked seizures and uncontrolled sensations in the body.
Epilepsy primarily impacts a person’s cognitive skills, affecting their ability to process information, relate, reason, and remember. It is one of the most prevalent nervous system disorders, affecting people of any age, ethnicity, race, or background.
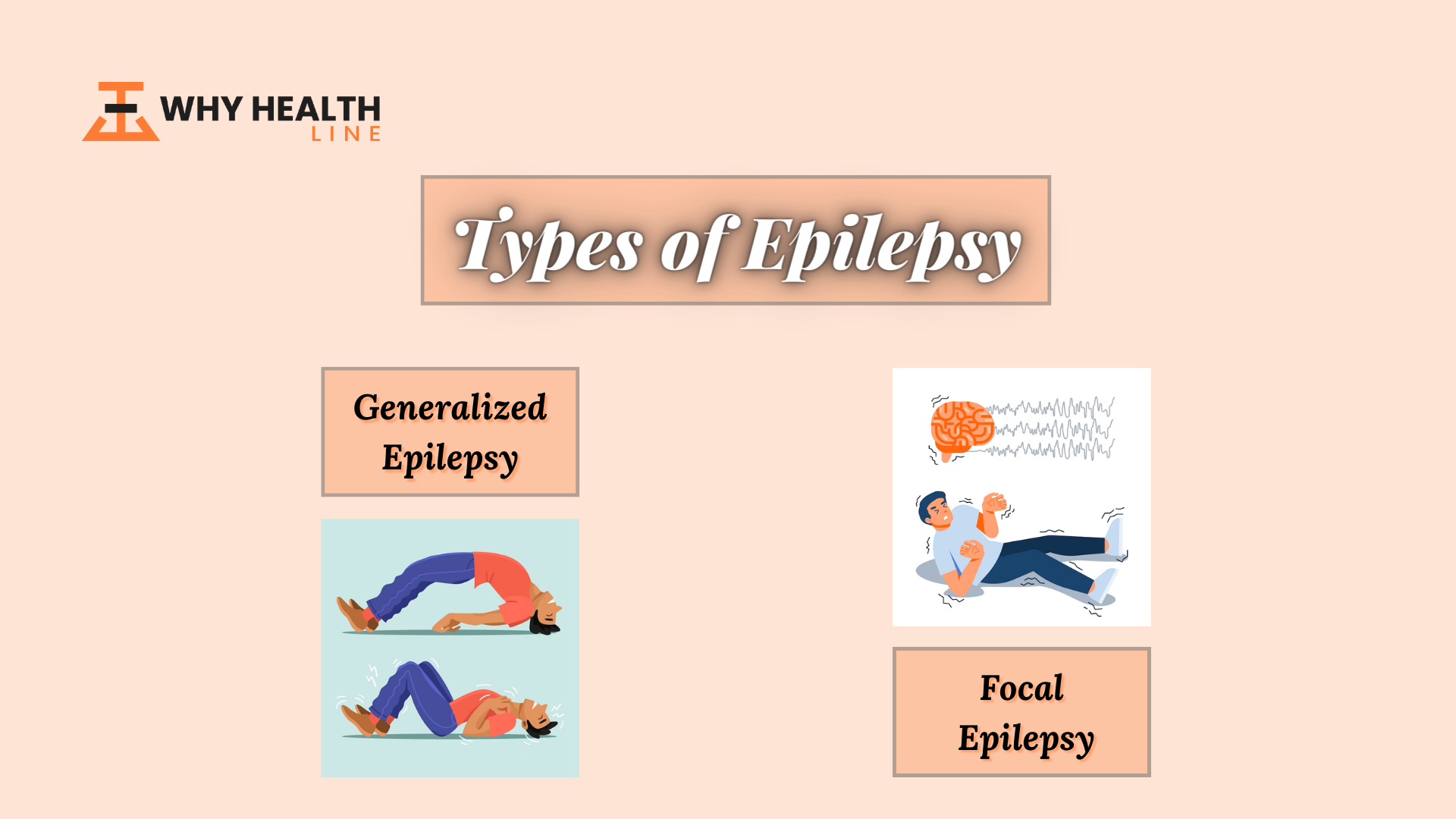
What Are the Different Types of Epilepsy?
There are many different kinds of epilepsy, some of which are completely harmless and barely noticeable. But others can be life-threatening.
This is because epilepsy disrupts brain activity, and its effects can spread to almost every part of the body.
-
Generalized Epilepsy
A generalized seizure typically lasts for 5 minutes or longer and is characterized as a medical emergency. If these seizures don’t stop or occur repeatedly, one right after another, then they can result in permanent injury or even death.
-
Focal Epilepsy
Focal epilepsy is a neurological condition in which seizures affect one side (hemisphere) of the brain. They occur when brain nerves are involved and affect a person’s ability to think and concentrate.
What Are the Symptoms of Epilepsy?
The main symptom of epilepsy is unconsciousness and repeated seizures. These sudden bursts of electrical activity in the brain temporarily affect how it works.
Seizures can affect people differently, depending on which part of the brain is affected.
- Staring.
- Jerking movements in different body parts, particularly in arms and legs.
- Stiffness in the body.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Breathing problems.
- Loss of bladder control.
- Falling suddenly with loss of consciousness.
Causes of Epilepsy
Doctors don’t know the actual cause of epilepsy. In some cases, certain brain conditions like tumors, imbalance of nerve-signaling chemicals, brain damage, or head injuries might be the reason behind these recurrent seizures.
How Is Epilepsy Diagnosed?
Epilepsy affects various parts of the human body as it is a brain disorder. However, it can be challenging to diagnose it because epilepsy is often confused with other problems, like panic attacks, unconscious falling, fainting, and migraines.
Mostly, to diagnose this disorder, doctors recommend an electroencephalogram (EEG). It is a test that can show unusual electrical activity in the brain that usually happens in patients suffering from epilepsy.
During this diagnostic procedure, doctors attach small sensors to the scalp of patients to pick up the electrical signals produced when brain cells communicate with neurotransmitters and send messages to each other.
How Is Epilepsy Treated?
The right treatment approach can help most people with epilepsy have fewer seizures or sometimes completely resolve the symptoms. Treatment options may include:
- Intake of medicines called anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs).
- Surgery removes a small part of the brain, which results in uncontrolled seizures.
- The placement of a small electrical device inside the body can minimize or control seizure attacks.
- Intake of a special diet (ketogenic diet) that can help control the repetition of seizures.
Risk Factors of Epilepsy
There are various complications associated with this brain condition:
- Difficulty learning.
- Severe or life-threatening injury from falls during a seizure.
- Permanent brain damage such as stroke and other disorders.
- Certain side effects of medications.
Key Takeaway
Epilepsy is a common brain disorder that can result in life-threatening situations. But with the right care and treatment, patients suffering from this condition can conduct a normal life.
However, depending on every patient’s experiences, it can be tricky to recognize when someone is having a seizure. Therefore it’s important to keep a check on symptoms.
If a person has lost consciousness, stares blankly, or appears as if he’s not listening, then it might be a sign of epilepsy. If any of your loved ones experience such symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
FAQs:
Can Patients With Epilepsy Live a Normal Life?
With the right treatment and proper management, patients with epilepsy can undoubtedly lead a normal life. However, if the symptoms don’t improve, the risk of early death can be relatively higher.
Epilepsy with recurrent seizures can also have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. Moreover, unprovoked seizures often accompany other issues, such as loss of awareness, depression, and learning disabilities.
How Serious Is Epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a serious brain disorder. If repeated seizures occur in epilepsy, permanent injury or sometimes even death can occur. Nevertheless, this problem can be prevented with prompt medical intervention.
Is Epilepsy a Brain Damage?
While mostly epilepsy does not result in permanent brain damage, sometimes it may lead to problems that ultimately impact an individual’s cognitive skills and brain structure.
Seizures can also result in the loss of specific brain cells but this is highly dependent upon the type of seizure and the underlying cause of epilepsy.