Oral cancer is a serious disease that affects thousands of people worldwide. It is a type of cancer that occurs in any part of the mouth, including:
- Lips
- Tongue
- Gums
- The roof of the mouth
In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatments of mouth cancer, as well as the steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing this disease.
Whether you are a current smoker, a heavy drinker, or simply looking to learn more about this important health issue.
This article will provide you with all the necessary information you need to protect yourself and your loved ones from oral cancer.
What Are the Symptoms of Oral Cancer?
The widely occurring symptoms of oral cancer are:
- Any internal mouth structures, such as the lips, gums, cheeks, or tongue, that exhibit swellings, thickenings, lumps, crusts, or erosions.
- White, crimson, or flecked velvet (white and red) areas of skin in the mouth.
- Oral melanoma.
- Sudden bleeding in the mouth.
- Any area of the mouth, neck, or face that feels uncomfortable, numb, or tender for no apparent reason.
- A discomfort or sensation of something being stuck in the throat.
- Difficulty speaking, moving the mouth or tongue, having trouble swallowing or chewing.
- Persistent sore throat, voice alteration, or hoarseness.
- An ear infection.
- Soreness or swelling in your jaw. If you wear dentures, it could be unpleasant or difficult to put them in.
- A dramatic decrease in weight.
Please contact your dentist or another healthcare provider immediately if you detect any of these changes.
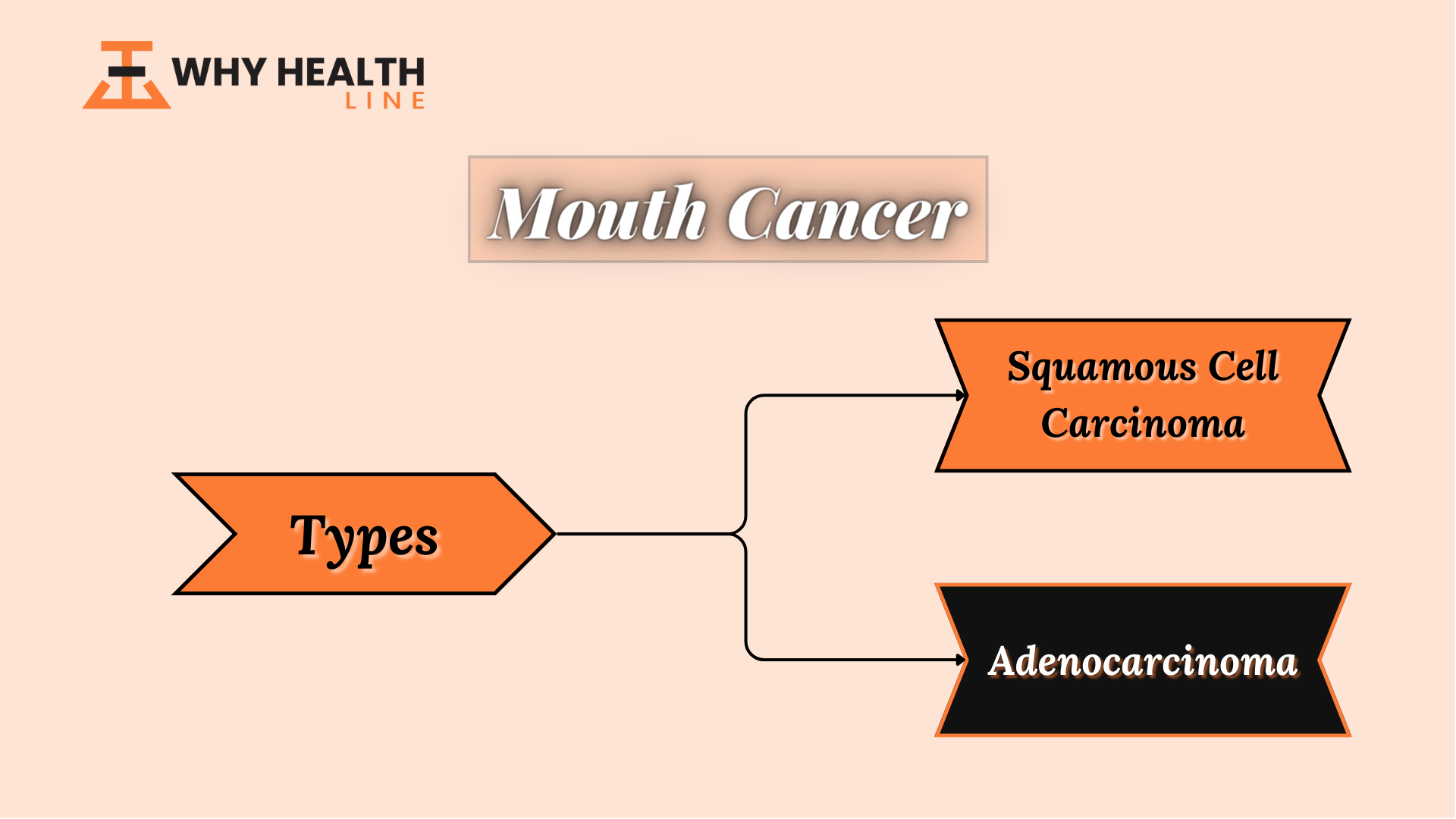
Types of Mouth Cancer
The type of cell cancer (carcinoma) that starts to grow helps to categorize mouth cancer.
-
Squamous Cell Carcinoma:
Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common type of oral cancer, occurring in nine out of ten cases. The skin and the mouth are two areas of the body where squamous cells are usually found.
-
Adenocarcinoma:
It affects the salivary glands. Sarcoma is a tumor that arises from abnormalities in bone, cartilage, muscle, or oral malignant melanoma.
These lymphomas occur as very dark, mottled swellings that frequently bleed, develop in the mouth, and originate from cells typically found in lymph glands.
How Do Healthcare Providers Diagnose Oral Cancer?
Dentists may find suspected oral cancer during routine checkups. They can recommend patients visit a head and neck or oral surgeon as well.
These professionals are also specialized in ENT (ear, nose, and throat) and can provide appropriate treatment for such problems.
Oral cancer tests include:
-
Physical Examination:
Your doctor will examine your mouth from top to bottom and may also feel around your mouth. Your head, face, and neck will also be administered for possible precancerous or cancerous growths.
-
Scrape Biopsy or Exfoliative Cytology:
Medical professionals gently scrape the affected area using a little brush or spatula to extract cells that will be analyzed for malignancy.
-
Incisional Biopsy:
Your healthcare professional will remove small tissue fragments so that cells can be obtained and tested for cancer.
Treatment for Mouth Cancer
With proper diagnosis and the right approach, mouth cancer can certainly be cured. Here are the main treatments for oral cancer:
-
Radiation Therapy:
Strong energy beams kill or stop the cancer cells’ growth. Radiation therapy may be used alongside other therapies, according to your healthcare professional.
-
Targeted Therapy:
This cancer treatment uses medications or other chemicals to accurately pinpoint and eliminate certain cancer cell types without harming healthy cells.
Laboratory-produced immune system proteins called monoclonal antibodies are utilized to treat cancer.
-
Chemotherapy:
Anti-cancer medications that kill cancer cells may be used by your doctor, including procedures that affect most of your body.
-
Immunotherapy:
Cancer is treated with immunotherapy, which activates your immune system to attack the condition. Sometimes the procedure is referred to as biological therapy.
Preventions for Mouth Cancer
The primary goal of treatment is to prevent mouth cancer while protecting vital oral functions, including breathing, speaking, and eating.
The three best methods to stop oral cancer from developing or returning after a successful course of therapy are:
- Avoiding tobacco use.
- Eating fish, citrus fruits, olive oil, and fresh vegetables, particularly tomatoes, as part of a healthy balanced diet.
- Minimizing alcohol intake.
- Going to routine dental examinations because the early stages of oral cancer are frequently detectable by a dentist.
FAQs
Does Mouth Cancer Cause Death?
Mouth cancer can become a reason for death if it is not detected and treated early. According to the American Cancer Society, approximately 9,750 people in the United States die yearly from oral and oropharyngeal cancers.
If detected early, the chances of successful treatment and survival are higher. Therefore, it is important to see a doctor or dentist if you have any symptoms or concerns about your oral health. Regular dental checkups and good oral hygiene can also help prevent oral cancer.
At What Age Does Mouth Cancer Occur?
Mouth cancer can occur at any age, but it is more commonly diagnosed in people over the age of 40, and the risk increases with age. In addition, men are more likely to develop mouth cancer than women.
Moreover, people who smoke or use tobacco products, consume alcohol excessively, have poor oral hygiene, have a weakened immune system, or have a family history of cancer are also at a higher risk of developing this type of cancer.